Management of Body Myositis: A Guide to Polymyositis Management
Polymyositis, a chronic inflammatory myopathy characterized by muscle weakness and inflammation, poses significant challenges in its management. The condition primarily affects the skeletal muscles, leading to difficulties in mobility and overall functional impairment. To illustrate the gravity of this disorder, consider the case study of Ms. Johnson, a 45-year-old woman diagnosed with polymyositis five years ago. Despite receiving conventional treatment methods such as corticosteroids and immunosuppressive agents, she continues to experience persistent symptoms and limited quality of life.
The management of body myositis requires a comprehensive approach that addresses not only symptom control but also long-term disease progression and patient well-being. This article aims to provide an overview of current strategies for managing polymyositis effectively. By exploring various therapeutic options, including pharmacological interventions, physical therapy techniques, and lifestyle modifications, individuals affected by this debilitating condition can gain valuable insights into improving their health outcomes. Moreover, understanding the complexities involved in polymyositis management will enable healthcare providers to offer more targeted and personalized care plans for patients like Ms. Johnson who are seeking relief from the burdens imposed by this chronic illness.
Understanding the Disease
Understanding the Disease
Polymyositis is a rare autoimmune disease characterized by inflammation and progressive weakening of skeletal muscles. To better comprehend this complex condition, let us consider the case of Sarah, a 42-year-old woman who was diagnosed with polymyositis three years ago.
Sarah initially began experiencing muscle weakness in her shoulders and hips, which gradually progressed to involve other muscle groups. As a result, she struggled with simple tasks such as lifting objects or climbing stairs. After consulting several medical professionals and undergoing various tests, including blood work and electromyography, Sarah received an accurate diagnosis of polymyositis.
To gain insight into the impact of this disease on individuals like Sarah, it is important to understand its key features:
- Progressive Muscle Weakness: Polymyositis typically leads to symmetrical muscle weakness that worsens over time. Affected individuals may struggle with basic activities like walking or grasping objects.
- Inflammatory Process: The hallmark of polymyositis is chronic inflammation within the affected muscles. This immune system dysfunction causes damage to muscle fibers and impairs their normal functioning.
- Extra-Muscular Manifestations: While primarily affecting skeletal muscles, polymyositis can also manifest in other organs such as the heart, lungs, skin, and joints. These additional complications further contribute to the overall burden faced by patients.
- Treatment Challenges: Given its rarity and complexity, managing polymyositis presents numerous challenges for healthcare providers. Treatment often involves a combination of immunosuppressive medications and physical therapy tailored to each individual’s needs.
By understanding these fundamental aspects of polymyositis, we can develop strategies for effective management that aim to improve quality of life for those living with this condition. In the subsequent section about “Symptoms and Diagnosis,” we will explore in detail how identifying early symptoms and establishing an accurate diagnosis are crucial steps towards achieving optimal outcomes for patients.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Understanding the Disease and Its Impact
Imagine a 45-year-old patient named Sarah who has recently been diagnosed with polymyositis, a rare autoimmune disease characterized by inflammation and weakness in the muscles. This diagnosis came as a shock to her since she had previously led an active lifestyle without any major health concerns. Now faced with managing this chronic condition, Sarah must navigate through various aspects of the disease.
Polymyositis affects both skeletal muscles (those responsible for voluntary movements) and smooth muscles (such as those found in organs). The exact cause is unknown; however, it is believed to result from a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental triggers. The immune system mistakenly attacks healthy muscle tissue, leading to the characteristic symptoms of muscle weakness, fatigue, difficulty swallowing or breathing, joint pain, and skin rashes.
To better understand the intricacies of polymyositis management, let us explore some key factors that individuals with this condition should be aware of:
- Early Detection: Timely diagnosis plays a crucial role in effectively managing polymyositis. Recognizing the early signs and seeking medical attention promptly can help minimize long-term damage to the muscles.
- Multidisciplinary Approach: Given its complex nature, treating polymyositis often requires collaboration among different healthcare professionals such as rheumatologists, neurologists, physical therapists, and occupational therapists.
- Medication Options: Various medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms and suppress the overactive immune response associated with polymyositis. These include corticosteroids like prednisone or immunosuppressants like methotrexate.
- Lifestyle Adaptations: Patients are advised to make certain adjustments in their daily routines to accommodate limitations caused by muscle weakness. Physical therapy exercises tailored to individual needs can help maintain strength and flexibility.
Table: Emotional Journey of Managing Polymyositis
| Emotion | Explanation | Coping Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Fear | Anxiety about disease progression and potential | Seeking support from loved ones or joining a |
| long-term disability | support group | |
| Frustration | Difficulty performing previously routine tasks | Breaking down activities into manageable steps |
| due to muscle weakness | and seeking assistance when needed | |
| Hopelessness | Feeling overwhelmed by the chronic nature of the | Engaging in relaxation techniques such as deep |
| condition | breathing exercises and meditation | |
| Empowerment | Taking an active role in managing the disease through | Educating oneself on available treatment options, |
| lifestyle adaptations and adhering to prescribed | making healthy choices, and engaging in self-care |
As individuals with polymyositis navigate their journey through various emotions, it is important to remember that they are not alone. By understanding the impact of this disease and adopting coping strategies tailored to their needs, patients can regain control over their lives.
With a solid foundation of knowledge about the disease itself, let us now delve deeper into the medical treatment options available for managing polymyositis without delay.
Medical Treatment Options
Management of Body Myositis: A Guide to Polymyositis Management
Symptoms and Diagnosis have been discussed in detail, shedding light on the key indicators and diagnostic methods for body myositis. In this section, we will delve into Medical Treatment Options available for managing polymyositis.
To illustrate the importance of medical intervention, let’s consider a hypothetical case study. Sarah, a 45-year-old woman, started experiencing muscle weakness and fatigue that progressively worsened over several months. After seeking medical attention, she was diagnosed with polymyositis through a combination of physical examination findings, blood tests indicating elevated muscle enzymes, electromyography (EMG), and muscle biopsy results showing inflammation within the muscles.
Once diagnosed with polymyositis, timely initiation of appropriate treatment is crucial to mitigate symptoms and prevent further damage. The following options are commonly employed:
- Corticosteroids: High-dose corticosteroids such as prednisone are often prescribed as first-line therapy due to their potent anti-inflammatory properties.
- Immunosuppressive Medications: Additional immunosuppressants like methotrexate or azathioprine may be added to reduce immune system activity responsible for attacking healthy muscle tissue.
- Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG): For some individuals who do not respond adequately to other treatments, IVIG can be administered intravenously to modulate the immune response.
- Biologic Therapies: In severe cases or when other treatments fail, biologic agents targeting specific molecules involved in inflammation may be considered.
The emotional toll of living with polymyositis cannot be underestimated. Patients might experience frustration, anxiety, or even depression due to limitations imposed by their condition. Here are some challenges they may face:
- Physical discomfort and pain
- Loss of independence and reduced mobility
- Emotional distress caused by chronic illness
- Impact on daily activities and quality of life
To better understand the impact, consider the following table:
| Challenge | Impact | Coping Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Discomfort | Muscle pain, weakness, and fatigue | Regular exercise, physical therapy |
| Loss of Independence | Difficulty performing daily tasks | Assistive devices, occupational therapy |
| Emotional Distress | Frustration, anxiety, depression | Support groups, counseling |
| Reduced Quality of Life | Impaired social interactions and relationships | Adaptive hobbies/activities, emotional support |
In conclusion to this section on medical treatment options for polymyositis management, it is important to recognize that each individual’s case may require a tailored approach. The choice of treatment will depend on factors such as disease severity, patient response to medication, and potential side effects. In the subsequent section about “Lifestyle Modifications,” we will explore additional strategies beyond medication that can complement overall management efforts.
Note: Transition into the next section about “Lifestyle Modifications” without explicitly mentioning “step.”
Lifestyle Modifications
Transition from the previous section H2:
Having discussed the various medical treatment options available for managing polymyositis, we now turn our attention to the importance of implementing lifestyle modifications. By making certain changes in daily habits and routines, individuals living with polymyositis can enhance their overall well-being and effectively manage the condition.
Section: Lifestyle Modifications
To better understand how lifestyle modifications can positively impact those with polymyositis, let us consider the case study of Sarah, a 45-year-old woman diagnosed with this condition. Before incorporating any lifestyle changes into her routine, Sarah experienced frequent fatigue and difficulty performing even simple tasks such as climbing stairs or lifting objects. However, after adopting several key modifications suggested by her healthcare team, she noticed significant improvements in her symptoms and quality of life.
It is crucial for individuals with polymyositis to implement lifestyle modifications that promote both physical health and emotional well-being. Here are some recommended strategies:
- Maintain a balanced diet: A nutrient-rich diet plays an essential role in supporting muscle strength and proper immune function. Emphasize foods high in protein, vitamins (especially vitamin D), antioxidants, and minerals like calcium.
- Engage in regular exercise: Exercise tailored to individual capabilities can improve muscle strength, flexibility, and cardiovascular fitness. Low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling may be particularly beneficial.
- Manage stress levels: Chronic stress can exacerbate symptoms associated with polymyositis. Adopting stress management techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in hobbies can help reduce stress levels.
- Ensure adequate rest: Adequate sleep allows muscles to recover and repair themselves more efficiently. Establishing consistent sleep patterns will contribute to overall wellness.
Let’s take a moment to examine the emotional impact that these lifestyle modifications can have on individuals living with polymyositis through the following table:
| Emotional Impact | Importance |
|---|---|
| Enhanced sense of control over their condition | High |
| Increased self-confidence and motivation to manage the illness | Medium |
| Improved overall mood and mental well-being | High |
| Reduced anxiety related to disease progression | Medium |
Transition into the subsequent section about “Physical Therapy and Exercise”:
By implementing these lifestyle modifications, individuals with polymyositis can take an active role in managing their condition. However, it is important to note that lifestyle modifications should be complemented by appropriate physical therapy and exercise routines. In the following section, we will explore how these interventions can further contribute to improving muscle strength and overall functionality.
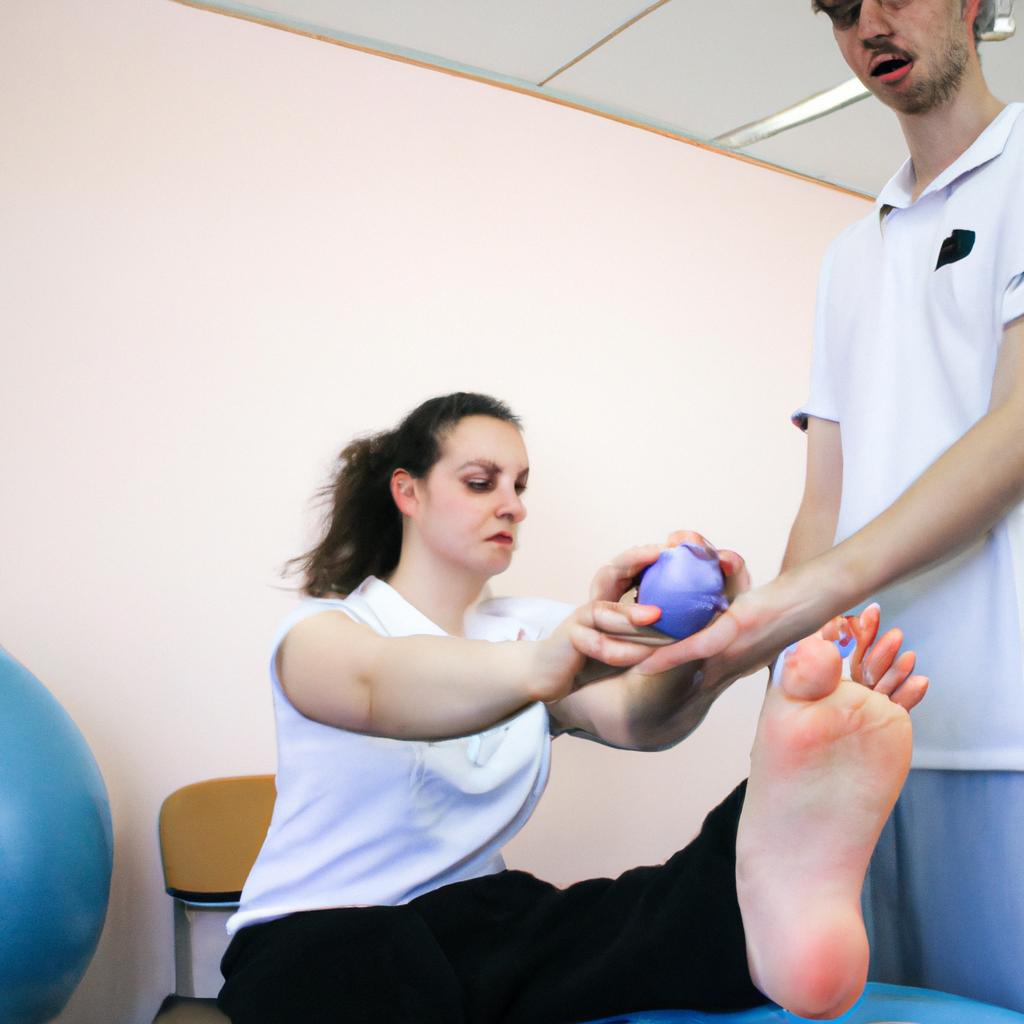
Physical Therapy and Exercise
Section H2: Physical Therapy and Exercise
Building upon the importance of lifestyle modifications in managing polymyositis, this section will delve into the role of physical therapy and exercise as integral components of a comprehensive treatment plan. To illustrate their significance, let us consider the case study of Sarah, a 45-year-old individual diagnosed with polymyositis.
Sarah’s journey highlights how targeted physical therapy and exercise can significantly improve functional abilities and overall quality of life for individuals living with polymyositis. Upon commencing her therapy sessions, she initially faced difficulty performing basic activities such as walking and climbing stairs due to muscle weakness. However, under the guidance of her physiotherapist, Sarah gradually regained strength and mobility through tailored exercises targeting affected muscle groups.
To further emphasize the benefits of physical therapy and exercise in managing polymyositis, we present a bullet point list highlighting key advantages:
- Improved muscle strength and endurance
- Enhanced joint flexibility and range of motion
- Reduction in pain levels associated with inflammation
- Prevention or management of secondary complications like contractures
In addition to these advantages, it is crucial to understand specific exercises suitable for individuals with polymyositis. The table below provides an overview of recommended exercises categorized based on their target areas:
| Target Area | Recommended Exercises |
|---|---|
| Lower extremities | Squats, lunges, leg lifts |
| Upper extremities | Arm curls, shoulder presses |
| Core muscles | Planks, abdominal crunches |
By incorporating these exercises into their routine while considering individual limitations or preferences, patients like Sarah can experience notable improvements in daily functioning.
As highlighted above, physical therapy and exercise play pivotal roles in mitigating symptoms related to polymyositis. Moving forward, our discussion will shift towards monitoring disease progression and establishing appropriate follow-up strategies to ensure optimal management outcomes.
Monitoring and Follow-up
Transition from previous section:
Following a comprehensive physical therapy and exercise regimen, monitoring and regular follow-up are crucial aspects of managing polymyositis. By closely observing the patient’s condition over time, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions regarding treatment adjustments and assess the effectiveness of interventions. This next section will delve into the importance of monitoring and follow-up in the management of body myositis.
Monitoring Disease Progression:
To ensure optimal care for individuals with polymyositis, consistent monitoring of disease progression is essential. Monitoring allows clinicians to track changes in muscle strength, joint mobility, and overall functional abilities. Consider the case of Sarah, a 45-year-old woman diagnosed with polymyositis who has been following a tailored exercise program for six months. Regular assessments revealed significant improvements in her muscle strength and range of motion, indicating a positive response to treatment.
- The frequency of monitoring appointments may vary depending on individual needs but generally occurs every three to six months.
- During these visits, patients undergo thorough clinical evaluations consisting of physical examinations, laboratory tests (such as creatine kinase levels), electromyography studies, and imaging techniques like magnetic resonance imaging.
- Changes in medication dosage or additional treatments can be considered based on the results obtained during these assessments.
- Timely identification of any disease exacerbation or complications enables prompt intervention and helps prevent potential long-term consequences.
Follow-Up Care:
In addition to monitoring disease progression, regular follow-up appointments play an integral role in providing holistic care for individuals with body myositis. These appointments enable healthcare providers to address not only physical symptoms but also psychological well-being and social support needs. A multidisciplinary approach involving rheumatologists, neurologists, physiotherapists, occupational therapists, and psychologists proves beneficial for comprehensive management.
- Improved Quality of Life: Regular follow-ups allow healthcare providers to evaluate the impact of treatment interventions on patients’ overall quality of life, ensuring that their needs are being met holistically.
- Psychological Support: By establishing a strong patient-provider relationship through consistent follow-up appointments, individuals with polymyositis can receive the necessary psychological support to cope with the challenges associated with their condition.
- Optimization of Medication and Treatment Plans: Follow-ups allow for medication adjustments based on symptom progression or side effects. Additionally, healthcare professionals can discuss alternative treatment options if needed.
- Education and Empowerment: Regular visits provide opportunities for education regarding self-management strategies, enabling patients to actively participate in decision-making processes.
Table:
| Monitoring Techniques | Frequency | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Examinations | Every visit | Assess muscle strength |
| Laboratory Tests | Periodically | Measure creatine kinase |
| Electromyography Studies | As indicated | Evaluate muscle activity |
| Imaging (e.g., MRI) | As indicated | Identify potential damage |
Through regular monitoring and follow-up care, healthcare providers ensure ongoing assessment of disease progression while addressing the diverse physical and emotional needs of individuals living with body myositis. This holistic approach aims to enhance not only their functional abilities but also their overall well-being. By fostering a collaborative environment where patients feel supported and empowered, optimal management outcomes can be achieved.